Carbon Offsetting Infographic: Everything You Need to Know about Carbon Offsets
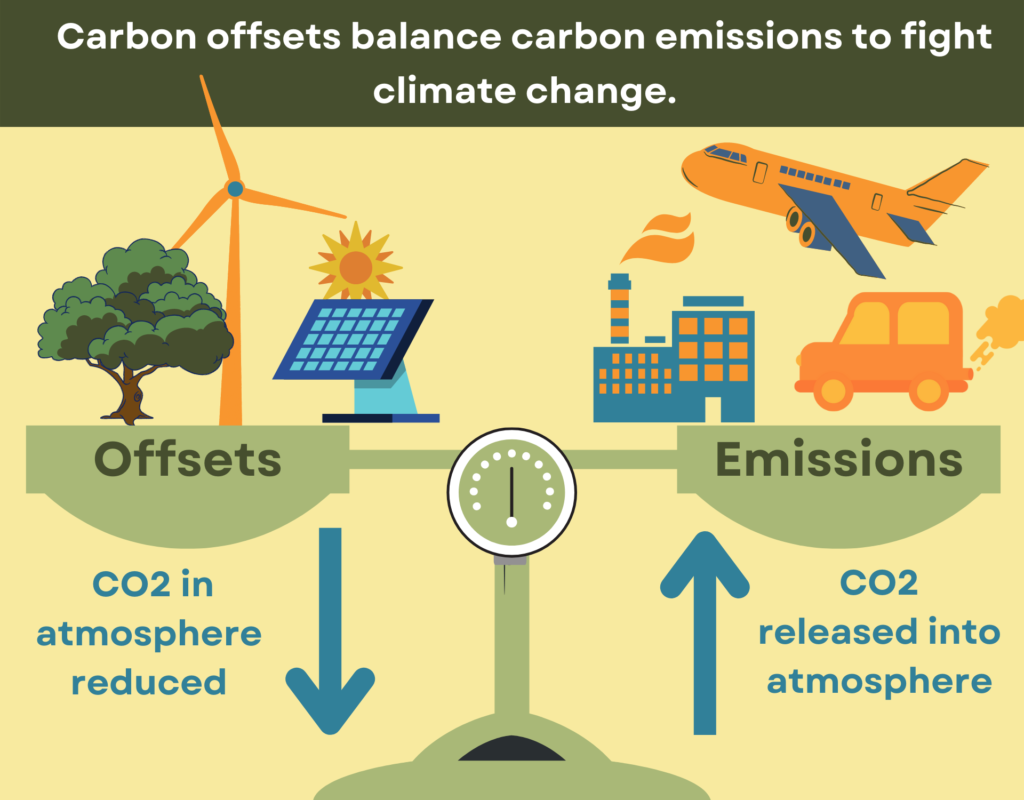
Carbon dioxide emissions are around 80% of all greenhouse gas emissions. Large amounts of greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere trap heat and cause global warming. In order to mitigate climate change, we need to reduce the amount of carbon dioxide we emit, or remove carbon dioxide that we’ve already emitted from the atmosphere.
Carbon offsets are actions that remove carbon from the atmosphere or prevent carbon from being released in order to “make up” for activities that release carbon and contribute to climate change. Individual people can buy offsets from organizations that support environmental projects in order to offset their personal carbon footprint. Businesses may choose to buy offsets voluntarily, or to offset emissions they produce that are above regulatory limits.
These carbon offsetting infographics will teach you the basics about carbon offsetting.

Types of Carbon Offsetting Projects
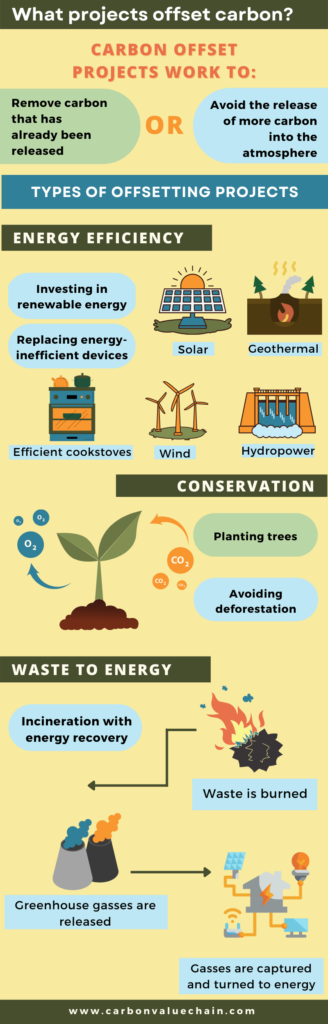
There are three main types of carbon offsetting projects:
- Energy efficiency:
- These projects focus on replacing carbon-intensive sources of energy, like fossil fuels, with renewable energy sources like solar panels, wind power, hydropower, and geothermal power (when heat is taken from the Earth and turned into energy).
- Energy efficiency projects may also work to replace carbon-intensive appliances with devices that use less energy or emit less carbon. For example, many carbon offset projects focus on clean cookstoves, or the replacement of wood-burning stoves (which release large amounts of carbon) with “clean” cookstoves. It’s important to note that these types of projects have mixed success rates, as this can sometimes result in more cooking overall, including on wood burning stoves, rather than simply switching to clean stoves entirely.
- Conservation:
- Conservation offsetting projects focus on protecting land that stores carbon, such as forests, in order to prevent further release of carbon. These projects may also plant trees in order to increase the amount of carbon stored in trees, and reduce the amount of carbon in the atmosphere.
- Waste to energy:
- Waste to energy involves disposal of waste that captures some of the greenhouse gases released from disposal. These types of offsetting projects not only reduce the amount of greenhouse emissions but also generate power. Waste to energy projects include capturing greenhouse gases like methane that are released from landfill or incineration and then turning those gases into energy, including heat, electricity or fuel. This process is often referred to as incineration with energy recovery.
While these are the main categories of carbon offsetting projects, any project that reduces greenhouse gas emissions or removes greenhouse gases from the atmosphere can be considered a carbon offset.
Further Reading
Learn more about solutions to reduce carbon and fight climate change:
- A Cost Benefit Analysis of the Carbon Tax: What Is It and What’s Its Purpose?
- The Impact of the Carbon Tax on Small Business
- How to Reduce Scope 3 Emissions: What Scope 3 Emissions Are and How Companies Can Address Them