Carbon Emissions from Urban Development

As our planet grapples with the pressing issue of climate change, urban development emerges as a significant contributor to the escalating levels of carbon emissions. With over 50% of the global population residing in cities, it is crucial to address the environmental impact of urbanization. Fortunately, there are sustainable urban planning and architectural solutions that offer hope for a greener, more sustainable future.
This article explores the challenges posed by carbon emissions from urban development. It discusses practical solutions that can help reduce these emissions while fostering a better quality of life for city dwellers.
The Urban Carbon Problem
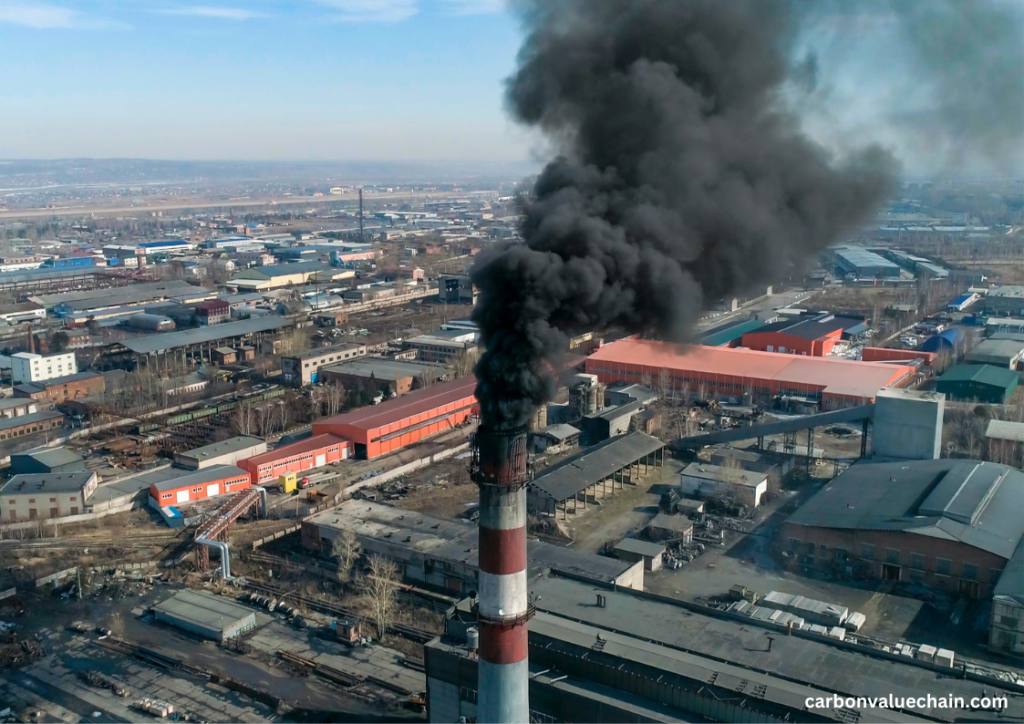
Urban areas are responsible for about 70% of global carbon emissions. The concentration of people, vehicles, industries, and infrastructure in cities makes them hotspots for emissions. From transportation to buildings, the urban landscape is intricately linked to carbon pollution. Here are some critical contributors to carbon emissions in urban development:
- Transportation: The combustion of fossil fuels in cars, buses, and other vehicles remains a significant source of urban carbon emissions. Traffic congestion, inefficient public transportation, and urban sprawl further exacerbate this issue.
- Energy Consumption: Buildings, both residential and commercial, are energy-hungry entities. Heating, cooling, and lighting consume vast amounts of energy, often derived from carbon-intensive sources like coal and natural gas.
- Waste Management: Waste disposal in cities generates methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas. Landfills and inadequate recycling systems contribute to these emissions.
- Industrial Activities: Urban areas often host industrial complexes, which can emit significant amounts of carbon through manufacturing and energy consumption.
Sustainable Urban Planning
To combat the rising carbon emissions from urban development, we need innovative and sustainable urban planning strategies prioritizing environmental conservation. Here are some critical elements of sustainable urban planning:
- Compact and Transit-Oriented Development: One of the most effective ways to reduce carbon emissions is through compact urban planning that encourages mixed land-use and transit-oriented development. This minimizes the need for long commutes, reduces the reliance on personal vehicles, and fosters walkable, bike-friendly neighborhoods.
- Green Spaces and Parks: Integrating green spaces into urban planning helps mitigate the urban heat island effect, improve air quality, and enhance residents’ well-being. Parks and green corridors act as natural carbon sinks, sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- Efficient Public Transportation: Investing in efficient and accessible public transportation systems can significantly reduce carbon emissions associated with personal vehicles. Well-designed transit networks make it easier for residents to choose eco-friendly modes of transport.
- Sustainable Infrastructure: Sustainable urban planning should incorporate resilient infrastructure that can withstand the challenges posed by climate change. This includes renewable energy sources, efficient water management, and green building technologies.
- Mixed-Income Housing: Sustainable urban planning should also focus on creating mixed-income neighborhoods to reduce urban sprawl and promote inclusivity. Such areas can be designed with energy-efficient and environmentally friendly features.
Architectural Solutions for Carbon Reduction
In addition to urban planning, sustainable architectural design is vital in reducing carbon emissions from urban development. Here are some architectural solutions that can help cities transition to a low-carbon future:
- Passive Design Principles: Architects can employ passive design strategies that utilize natural resources like sunlight and wind to heat, cool, and ventilate buildings. This minimizes the need for energy-intensive heating and cooling systems.
- Green Building Materials: Sustainable architecture promotes the use of eco-friendly, locally sourced, and recycled building materials, reducing the carbon footprint of construction. This includes bamboo, reclaimed wood, and low-VOC (volatile organic compounds) paints.
- Energy Efficiency: Designing buildings with energy efficiency in mind is essential. This involves using high-quality insulation, energy-efficient windows, LED lighting, and smart building management systems to minimize energy consumption.
- Renewable Energy: Integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, into building design can significantly reduce a building’s carbon emissions. Net-zero and carbon-positive buildings aim to produce more energy than they consume.
- Green Roofs and Vertical Gardens: Incorporating green roofs and vertical gardens into buildings not only reduces the urban heat island effect but also enhances the aesthetic appeal of the city while sequestering carbon dioxide.
- Rainwater Harvesting: Capturing and reusing rainwater for landscaping and flushing systems can reduce water consumption and alleviate stress on urban water infrastructure.
- Adaptive Reuse: Preserving and repurposing existing structures rather than demolishing and rebuilding can save energy and reduce waste. Adaptive reuse is an eco-conscious approach to architecture.
Examples of Successful Sustainable Urban Development
Several cities worldwide have implemented sustainable urban planning and architectural solutions to reduce carbon emissions. These case studies demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of such approaches:
- Copenhagen, Denmark, is known for its extensive network of bike lanes, abundant green spaces, and highly efficient public transportation system. This combination has not only kept carbon emissions impressively low but also ensured a high quality of life for its residents.
- Vancouver, Canada, has made a name for itself by implementing rigorous building codes and actively promoting green architecture. These measures have resulted in significant reductions in carbon emissions per capita, showcasing the city’s commitment to sustainability.
- Curitiba, Brazil, is renowned for its innovative urban planning. It is characterized by a meticulously designed public transportation system and a vast network of green spaces that provide residents with a unique and sustainable living environment.
- Singapore has taken a comprehensive approach to sustainability, seamlessly integrating green technologies into its urban landscape and prioritizing investments in energy-efficient buildings and renewable energy sources. This holistic strategy reinforces Singapore’s commitment to a more environmentally friendly and sustainable future.